We do not really know when the main building on Eid (local/oral/original name) or Eide (Danish spelling) was erected. However, we do have some clues.
The purchase contract of January 16, 1759 describes in detail the demarcation lines and all values included as Mette Christine Høyer, the widow of Austrått's owner Søren Dass, sells the farms Eide and Furunes (which both up to that point were part of the Austrått estate), with the salmon fishing rights and the island Brattingen, to "the royal bailiff over Fosen bailiwick, Johan Rüberg" for 600 riksdaler.
The puchase contract states that the Furunes farm has been deserted for a long time, unlike Eide (which always had inhabitants) and it says that "...and no houses on either of these farms". This part is actually a bit ambigous, but the contract is otherwise very detailed regarding the values and assets of the farm, so one would think the buildings would at least be mentioned, had they been worth mentioning.
The magistrate Peder Sivertsen Barup also lived on Eid(e) for twenty years; he rented the farm from the Austrått estate from 1723 to 1743. It is reasonable to think that even the magistrate had to live stately. However, 16 years later the contract of purchase transferring the Eide/Furunes estate from Mette Høyer (Austrått's owner) to the magistrate's successor as the inhabitant of the farm, bailiff Johan Rüberg, there is no mention of the buildings.
Therefore one might reason that bailiff Rüberg, who is now the owner of the Eide estate (unlike magistrate Barup, who never owned the farm), decides to erect some stately buildings on the farm. At some point he sells his farm to a second magistrate, Ove Schjelderup von Hadeln, magistrate of Fosen from 1764 to 1800. Rüberg dies in 1773. Some time between 1764 and 1773 the farm is trasferred to magistrate von Hadeln, and it is not too farfetched to assume that he finishes the building project. And very likely: with a vengeance.

I am allowing a small leap of faith here, but to me it seems likely that von Hadeln was tempted to reach into the cookie jar, i.e. the tax money he collected, to finish his grand estate. Von Hadeln was suspended from his office in 1792 because of several remarks about the way he ran his office, and he was declared bankrupt before he died in 1800. In 1801 the farm is foreclosed (and bought by the forefather of the current owners).
The picture shows the family Von Hadeln's coat of arms.
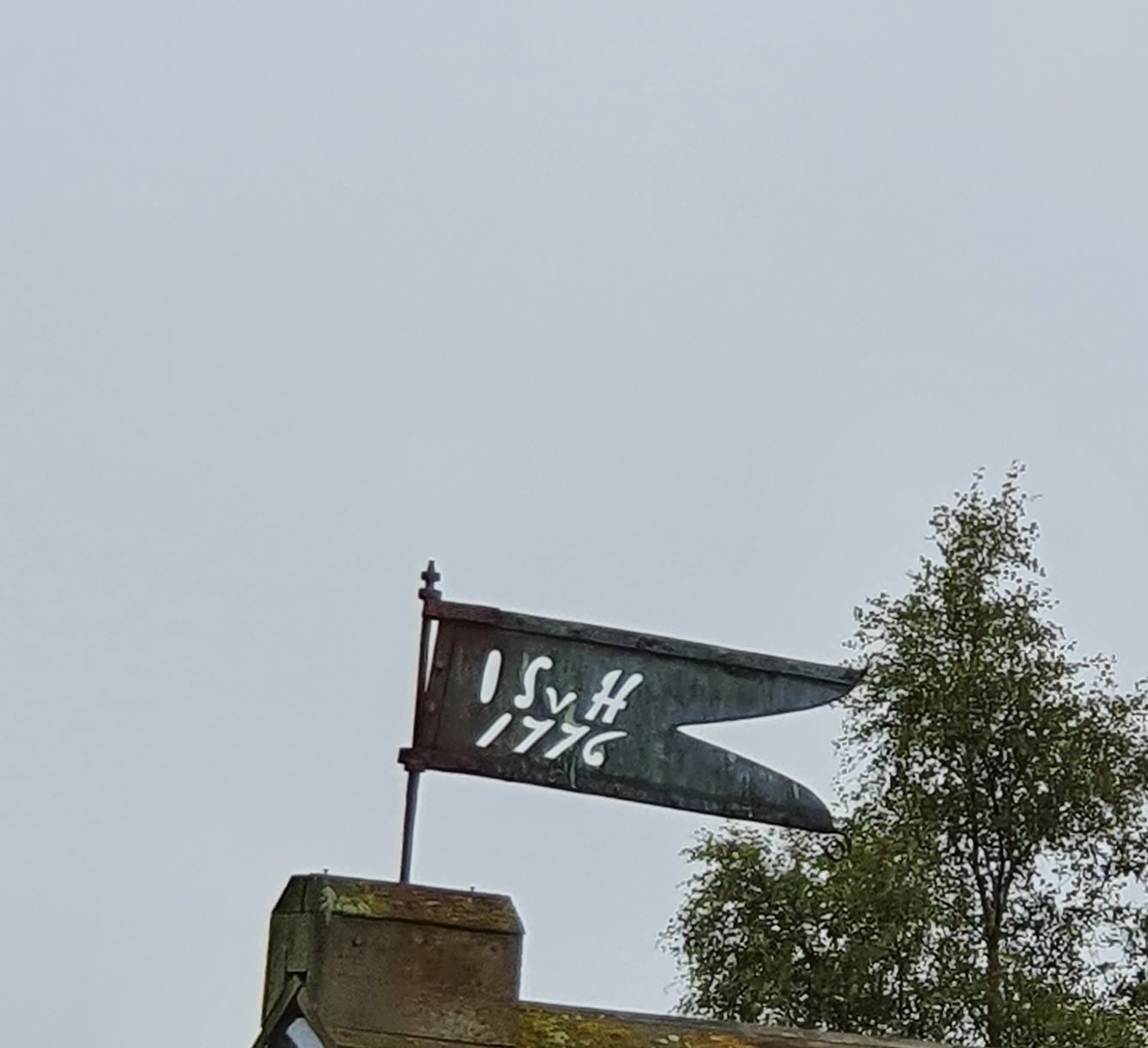

We can also reasonably assume that the main building was finished by 1776. One rather artistic metal weathervane still exists at the farm with von hadeln's initials (OSvH, Ove Schjelderup von Hadeln) and the year 1776. We take this to signify the finished status of the main building.
This weathervane still tells its story from the roof top of Nordstua.

In 1821 the farm was split into two parts (cf. the post about Johan Arnt), and one half of the buildings were allotted to each of the farms. Some of the structures were thus moved from East farm to West farm (specifically from Nergården to Øvergården).
There is a whole lot we do not know about how the buildings used to look and how big they used to be.
But there are also a couple of things we do know. Everything built for human accomodation in this period is classified as a "trønderlån". This is an effect of the capacity of the Norwegian saw mills, they could only accomodate logs 6 meters long. later saw mills can accomodate 7 meter long logs, and the houses accordingly get one meter wider.
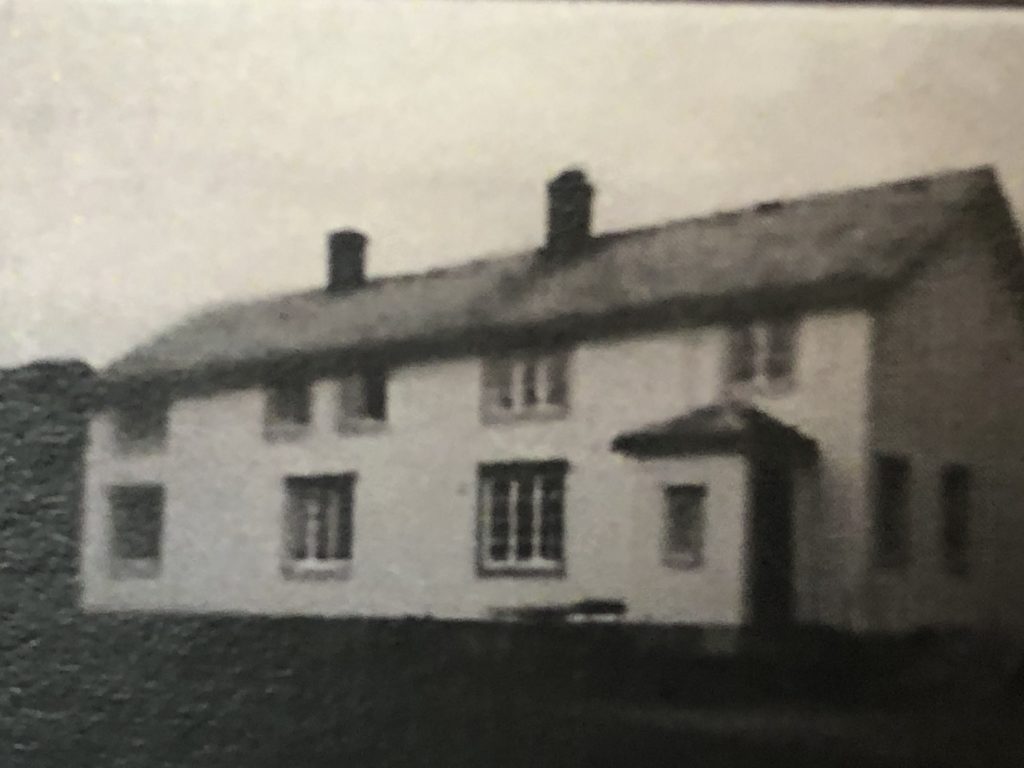
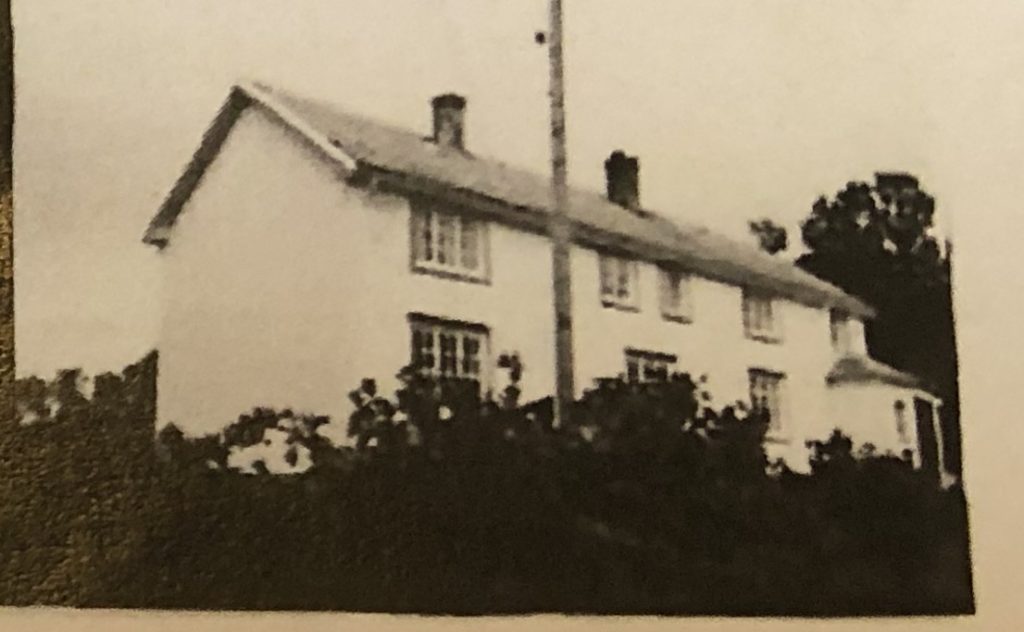
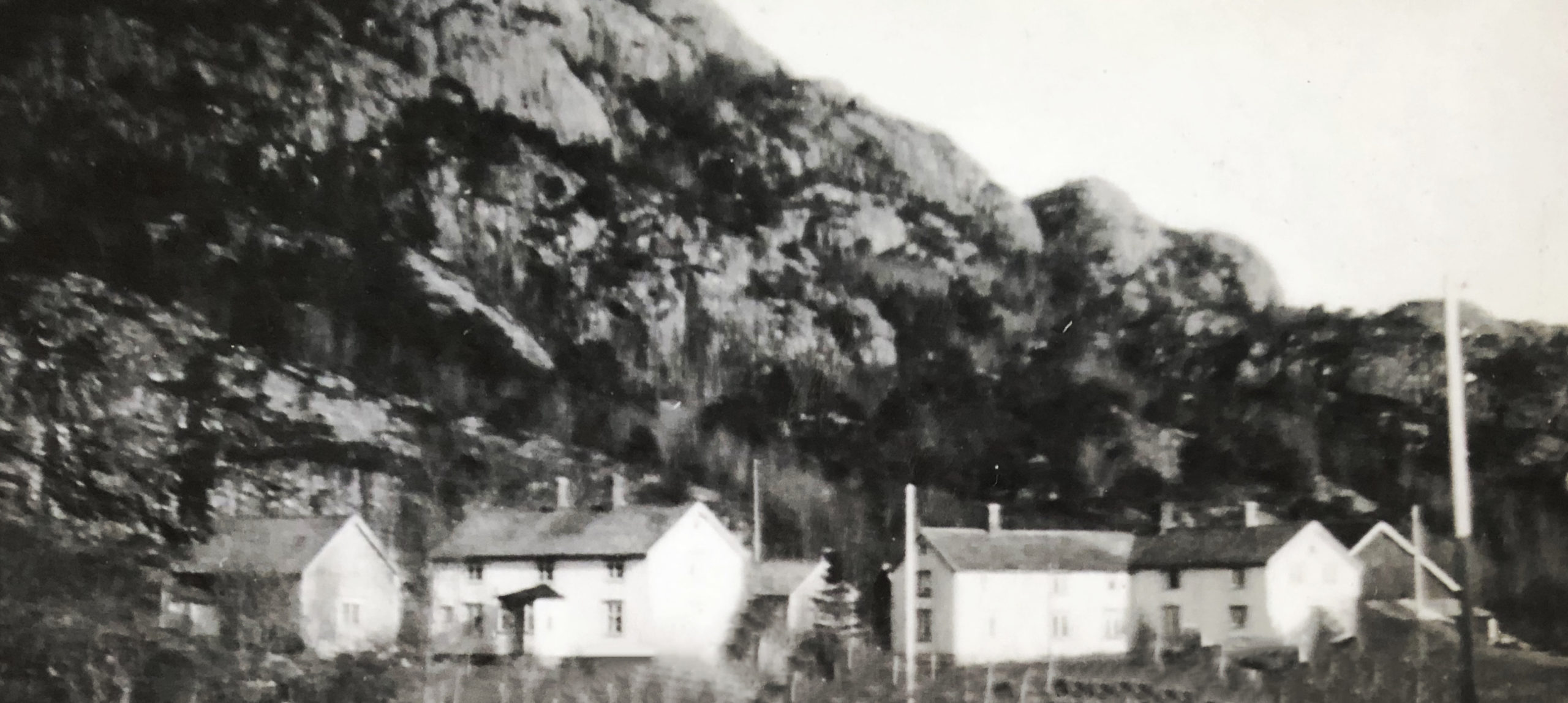
The main building on Eid was still rather special. We have pictures from 1901 and later showing that the main building at this time boasts two wings: It was build in an L-shape.

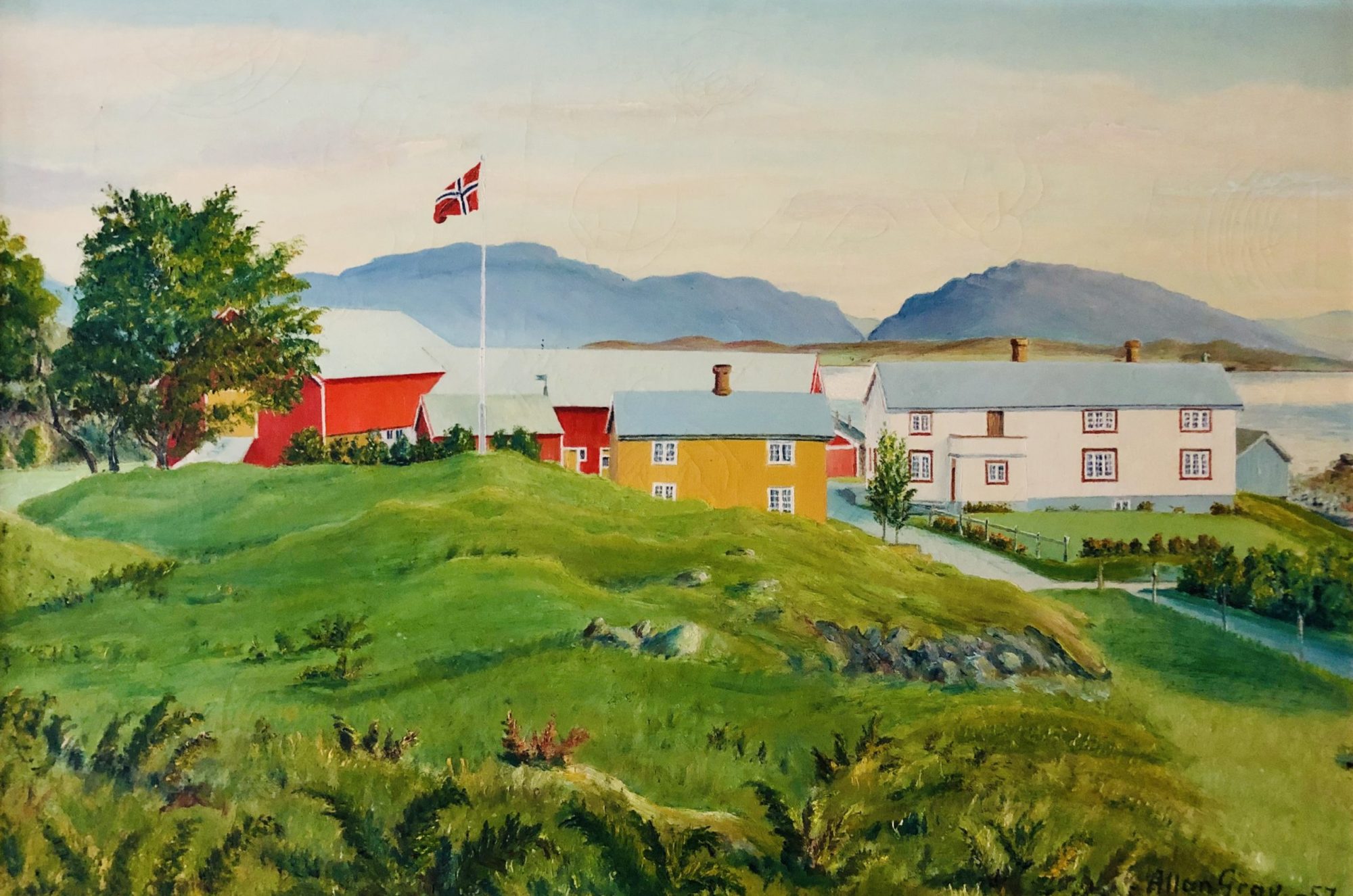
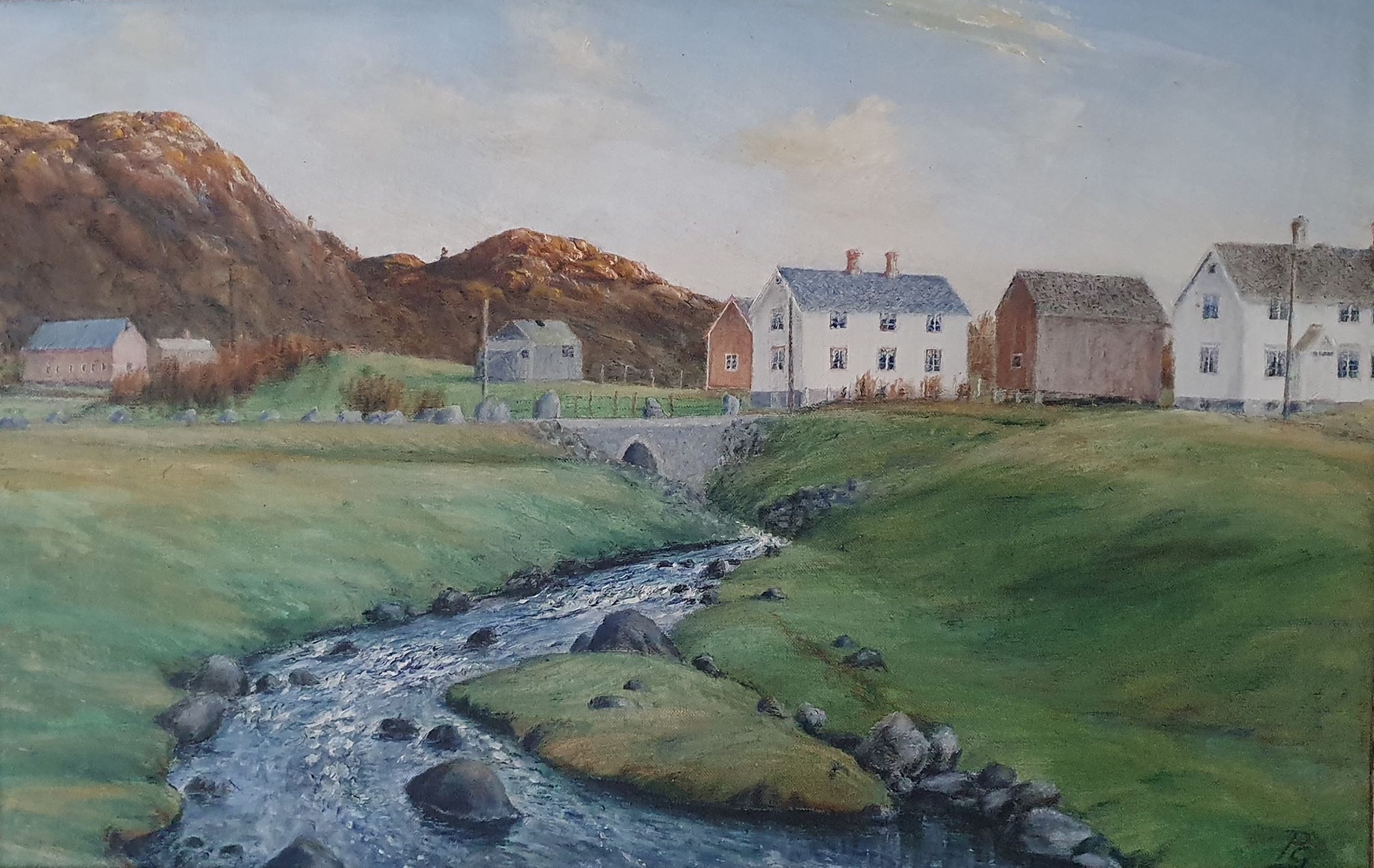
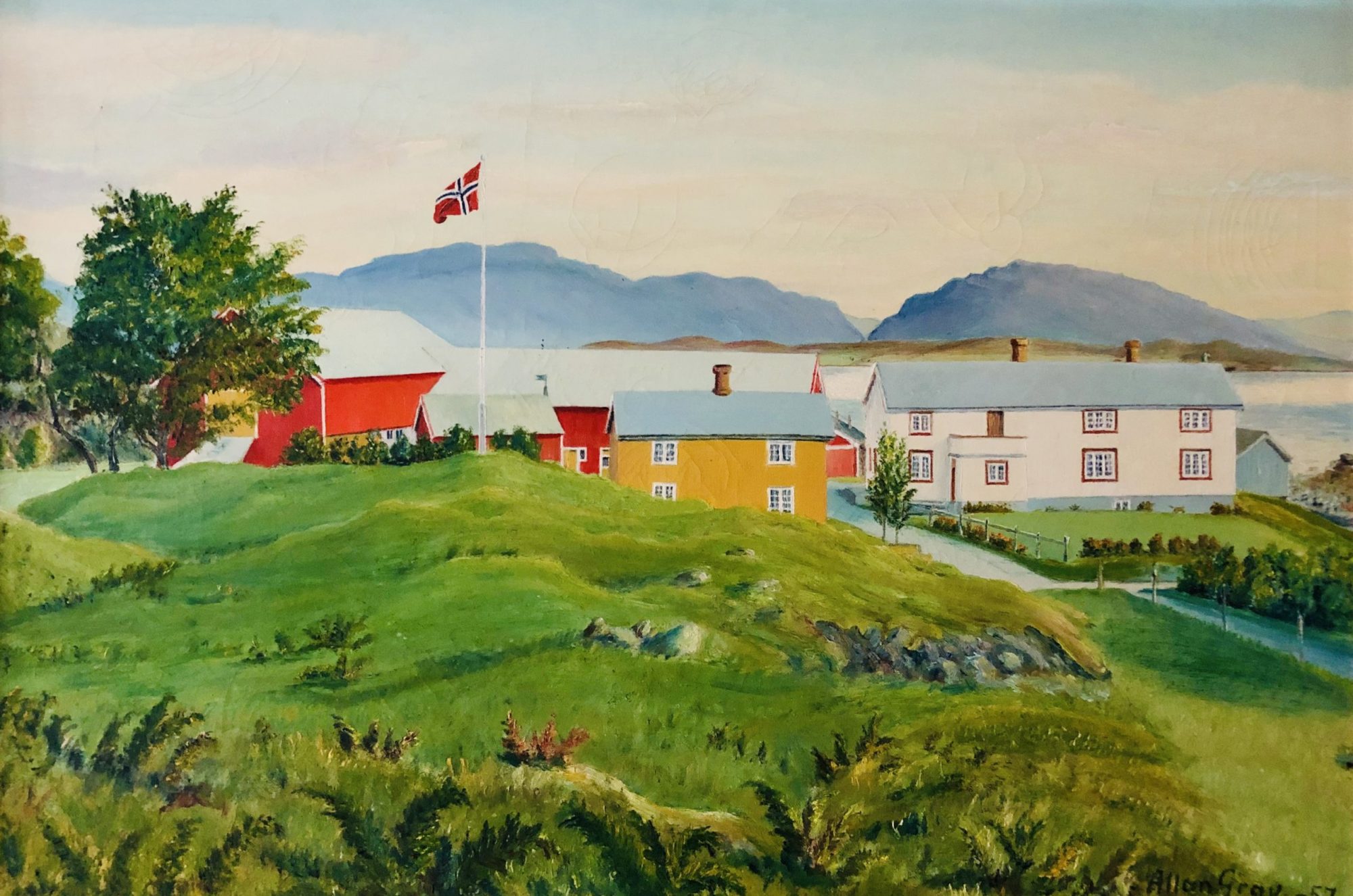
This picture displays how the road cuts through the yard, South of the L-shaped main building. The road was moved north of the main building in 1920, equipped with a new bridge. Gabriel builds himself a small house in 1924 north of this new road, thus the road still runs between some of the buildings on the farm. Gabriel's small house and the black smithy are at this point both north of the new road (cf. the painting below).



Entry from "Norwegian estate" revealing a great deal of important facts about the buildings and rebuildings of the farm, e.g. the renovation in 1948 and many other pivotal pieces of information.
We also find interesting figures over the amount of people and animals living on the farm.
The picture is taken from a rather unusual angle, from down by the river delta. Compare to the painting by Paul Grav above, displaying the farm from a similar angle.
As mentioned above, in 1947-1948 the main building undergoes a thorough transformation, and several of the buildings are altered and moved. The north wing of the main building is partly moved (Nordstua), one section is demolished, and the remainder of the building is extended and made longer and wider. The roof is also lifted so the ridge is still in center on the roof top, However, the chimneys are no longer centered at this ridge, instead they remain a bit to the south of the ridge. Nordstua (yellow building on the painting below) now becomes a separete annex which is rented out to various families as accomodation for the next couple of decades.

The storehouse is also moved, from the river's edge to a different location in the yard. This storehouse is later demolished (ca. 1979-1980) to give way to a new tractor stall.
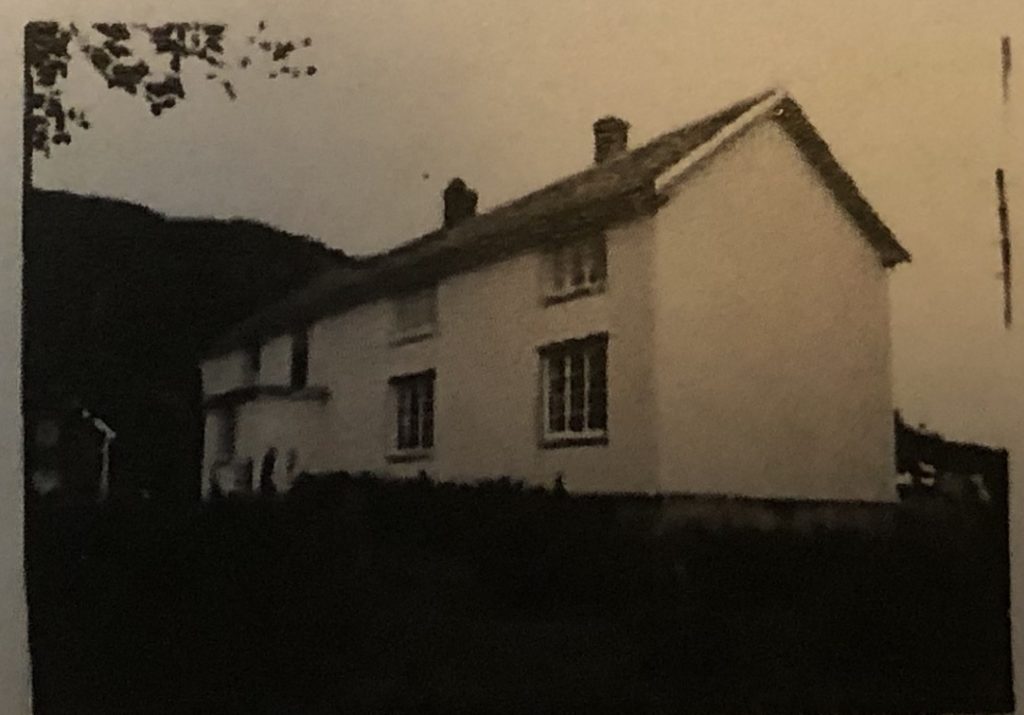
The little entrance on the south wall shown on the two pictures to the left from 1978 is torn down and replaced by a slightly bigger structure in 2001, this is used as the main entrance at that point.

As we started renovating the main building we wanted to replace the guest entrance at the north wall. This entrance has been used altogether about one dozen times for the last fourty years, each time for very distinguished guests.
To us this did not legitimize the immense waste of space for useless hallways resulting from this arrangement. We wanted to utilize the building structure much more efficiently. Accordingly, we submitted an application to the relevant auhtorities to demolish this small entrance and to erect a new structure for the main entrance, two stories high and also including a basement.
As mentioned above, the main buiding (like several other buildings on the farm) is registered as an entity of cultural heritage since 1978 (cf. the pictures above) and accordingly the county governor's office of cultural heritage perservation has a say in matters like ours. The official representative came for a thorough inspection (he even scrutinized the beams in the attic), and then made his official recommendation: You should construct two smaller entrance structures on the south wall, mimicking the features from 1901, and also move Nordstua back to the vicinity of the north wall, partially recreating the old L-shape of the old main building.
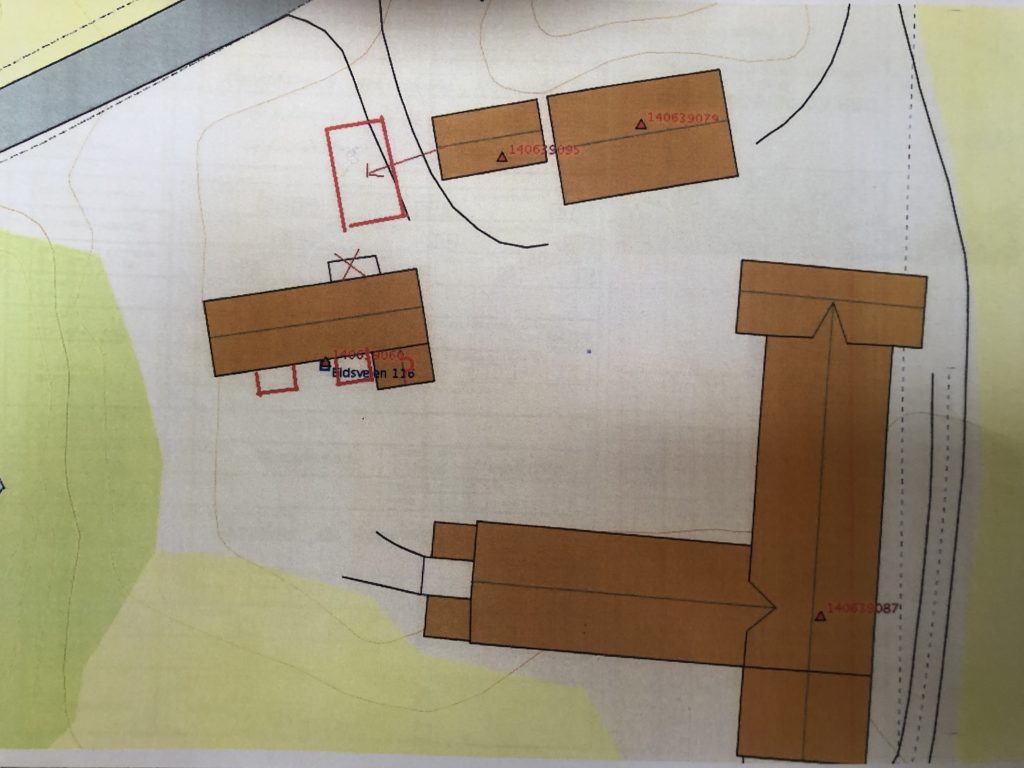
We considered this to be an impossible solution; this arrangement would imply an outline almost as impractical as the current one. The main entrance (or the TWO entrances!) would face the yard rather than the public road (introvert rather than extrovert!). Also, the authority for public roads had extended us the dispensation from ordinary regulations and allowed us to build the extension we wanted, but there was no way they would allow the placement of a cultural heritage building (the core of Nordstua possibly stems from the 17th century) this close to a public road. And worse: We would not want them to.
Another round of appealing, applying, providing new information and new arguments. The local authorities' views on these matters were more or less identical to our own. The result of this expensive renovation should be a modern building suited to house a modern family, not a museal structure solely suited for exhibitions and guided tours. At least not as its only function.
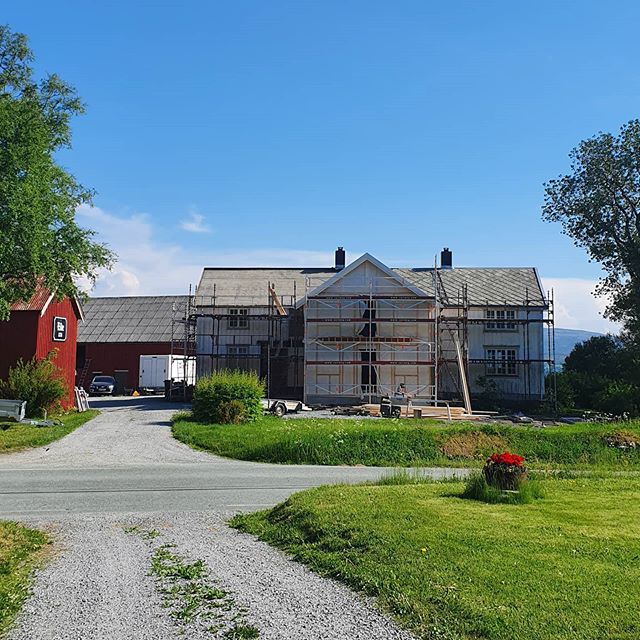

This is the north wall with the new extension. Planking and some windows are still missing on this picture. New pictures will come eventually, and the post might be updated.







